Exploring The Electromagnetic Spectrum: From Lowest To Highest Energy
Picture this: You're sitting on your porch, sipping coffee, and enjoying the morning sun. But did you know that the sunlight you're basking in is just a tiny part of something much bigger? Yep, we're talking about the electromagnetic spectrum! This invisible world of waves stretches far beyond what our eyes can see, from super-low energy waves to mind-blowing high-energy ones. So, let’s dive deep into this fascinating topic, shall we?
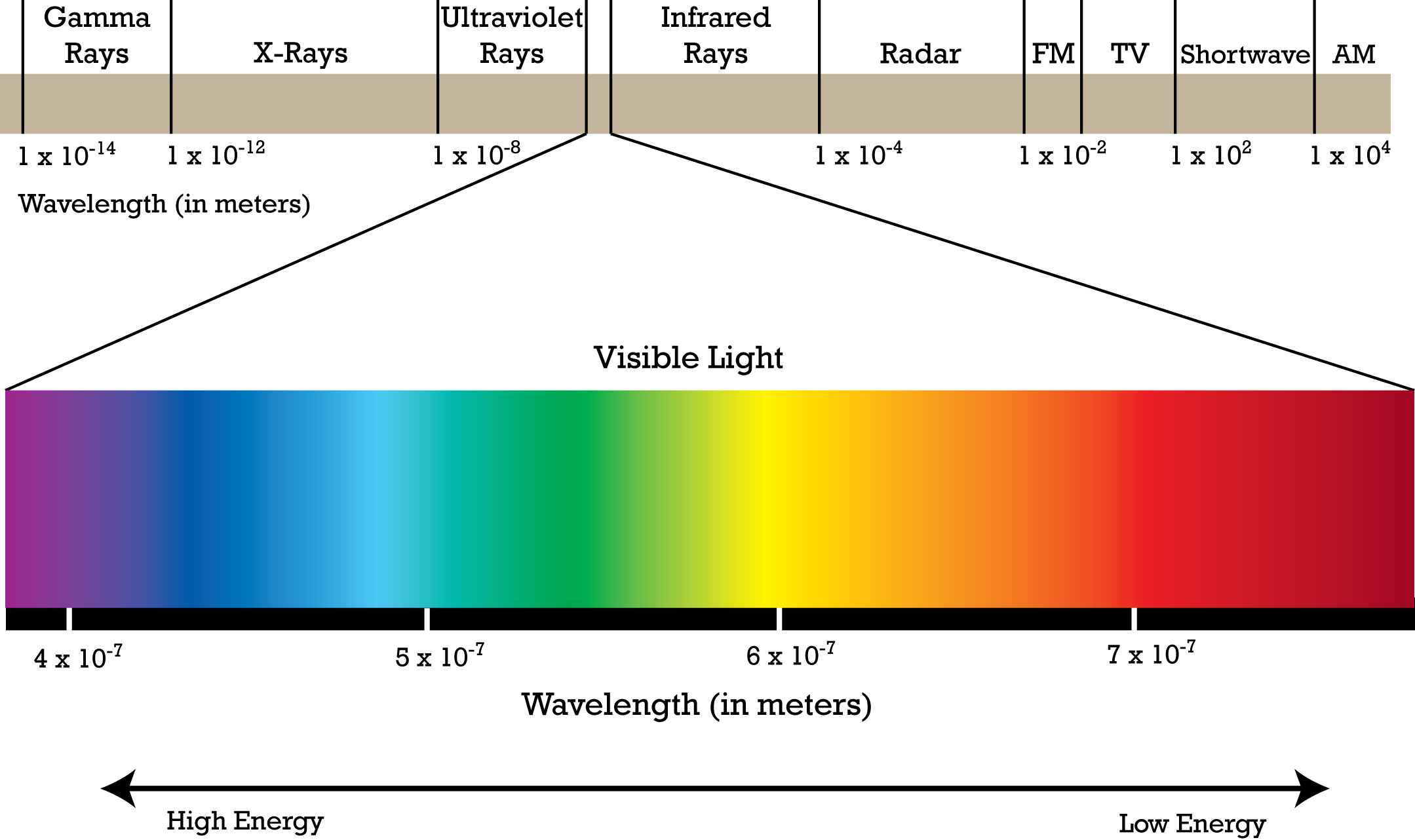
The electromagnetic spectrum from lowest to highest energy is like a giant cosmic ladder, where each rung represents a different type of wave. And guess what? These waves are everywhere—zipping through space, bouncing off walls, and even passing right through you. It’s kinda wild when you think about it. But don’t worry, we’ll break it down step by step so it’s easy to digest.
Now, why should you care about all this? Well, understanding the electromagnetic spectrum isn’t just for scientists in lab coats. It impacts your daily life more than you might think. From the radio waves that play your favorite tunes to the X-rays that help doctors see inside your body, this spectrum is the backbone of modern technology. So, let’s get started and unravel the mysteries of these incredible waves.
- Egusi And Fufu The Ultimate Nigerian Delight You Need To Try
- Butter Picture The Ultimate Guide To Capturing The Creamy Goodness
What Exactly is the Electromagnetic Spectrum?
Alright, let’s start with the basics. The electromagnetic spectrum is basically a big ol’ range of waves that carry energy. These waves travel at the speed of light and vary in wavelength and frequency. Think of it like a rainbow, but instead of colors, we’ve got waves with different energies.
Here’s the kicker: the spectrum includes everything from super-long radio waves to super-short gamma rays. And each type of wave has its own unique properties and uses. For example, radio waves are perfect for broadcasting music, while gamma rays can zap cancer cells. Cool, right?
Breaking Down the Spectrum: From Low to High Energy
Let’s take a closer look at the different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, starting from the lowest energy waves and working our way up. This is where the fun begins!
- Penn Station Nyc To Jfk Your Ultimate Guide To A Seamless Journey
- Dove Y Damiano The Ultimate Guide To Love Relationships And Modernday Romance
Radio Waves: The Long-Distance Runners
At the bottom of the spectrum, we’ve got radio waves. These are the longest waves and carry the least amount of energy. They’re the reason you can listen to your favorite tunes on the road or catch the latest sports game. Radio waves are also used for radar, communication with satellites, and even WiFi signals.
- Wavelength: Several meters to kilometers
- Frequency: 3 kHz to 300 GHz
- Uses: Broadcasting, communication, navigation
Microwaves: Heating Up the Action
Next up, we’ve got microwaves. These waves are shorter than radio waves and pack a bit more energy. You might know them best for their role in heating up your leftover pizza, but they’re also used in radar systems and satellite communication.
- Wavelength: 1 mm to 1 meter
- Frequency: 300 MHz to 300 GHz
- Uses: Cooking, radar, satellite communication
Stepping Up: Infrared Waves
Now we’re moving into the invisible world of infrared waves. These waves are just beyond what the human eye can see, but you can feel their heat. Infrared waves are used in everything from night vision goggles to remote controls.
But wait, there’s more! Infrared waves also play a big role in climate science, helping scientists study the Earth’s atmosphere and detect changes in temperature.
Visible Light: The Part We Can See
Finally, we’ve reached the part of the spectrum that’s visible to the human eye. This is where things get colorful! Visible light is made up of all the colors of the rainbow, and it’s the reason we can see the world around us.
- Wavelength: 380 nm to 750 nm
- Frequency: 400 THz to 790 THz
- Uses: Lighting, photography, fiber optics
UV Rays: Beyond the Rainbow
Once we move past visible light, we enter the world of ultraviolet (UV) rays. These waves are more energetic than visible light and can cause sunburns if you’re not careful. But UV rays also have some cool uses, like sterilizing medical equipment and detecting counterfeit money.
X-Rays: Seeing Through the Surface
Now we’re getting into the high-energy zone with X-rays. These waves are powerful enough to penetrate through soft tissues, making them perfect for medical imaging. But be careful—too much exposure can be harmful.
- Wavelength: 0.01 nm to 10 nm
- Frequency: 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz
- Uses: Medical imaging, security screening
Gama Rays: The Big Finish
And finally, we’ve reached the top of the spectrum with gamma rays. These are the most energetic waves and are often associated with nuclear reactions and cosmic events. They’re powerful enough to kill cancer cells but can also be dangerous if not handled properly.
Applications of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
So, why is the electromagnetic spectrum so important? Well, it’s the foundation of modern technology. From communication to medicine, the applications are endless. Here are just a few examples:
- Radio waves: Broadcasting, satellite communication
- Microwaves: Cooking, radar systems
- Infrared: Night vision, remote controls
- Visible light: Lighting, photography
- UV rays: Sterilization, counterfeit detection
- X-rays: Medical imaging, security screening
- Gamma rays: Cancer treatment, nuclear energy
Understanding the Science Behind It All
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s talk a little about the science behind the electromagnetic spectrum. It all comes down to two key factors: wavelength and frequency. Longer waves have lower frequencies and less energy, while shorter waves have higher frequencies and more energy.
And here’s a fun fact: all these waves travel at the same speed—the speed of light! But their energy levels vary depending on their wavelength and frequency. Isn’t science amazing?
How Do We Measure the Spectrum?
Scientists use special tools to measure the different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. For example, they use telescopes to detect radio waves and infrared cameras to capture heat signatures. These tools help us understand the universe and develop new technologies.
Real-World Impacts of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum isn’t just a theoretical concept—it has real-world impacts that affect our daily lives. From improving medical treatments to advancing communication technologies, the applications are vast and varied.
For example, MRI machines use powerful magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body. And GPS systems rely on microwave signals to pinpoint your location with incredible accuracy. These are just a few examples of how the electromagnetic spectrum is shaping the future.
Environmental Impacts
But it’s not all sunshine and rainbows. The electromagnetic spectrum can also have negative impacts on the environment. For example, excessive use of radio waves can interfere with wildlife communication, and overexposure to UV rays can harm ecosystems.
Conclusion: Why You Should Care
So, there you have it—a deep dive into the electromagnetic spectrum from lowest to highest energy. From radio waves to gamma rays, each part of the spectrum plays a vital role in our world. Understanding this invisible world can help you appreciate the technology around you and make informed decisions about your health and environment.
Now it’s your turn! Leave a comment below and let us know what part of the electromagnetic spectrum fascinates you the most. And don’t forget to share this article with your friends and family. Together, we can spread the knowledge and inspire the next generation of scientists!
Table of Contents
- What Exactly is the Electromagnetic Spectrum?
- Breaking Down the Spectrum: From Low to High Energy
- Radio Waves: The Long-Distance Runners
- Microwaves: Heating Up the Action
- Stepping Up: Infrared Waves
- Visible Light: The Part We Can See
- UV Rays: Beyond the Rainbow
- X-Rays: Seeing Through the Surface
- Gama Rays: The Big Finish
- Applications of the Electromagnetic Spectrum


Detail Author:
- Name : Dolly Schiller
- Username : ydavis
- Email : price.stokes@hotmail.com
- Birthdate : 1999-05-27
- Address : 560 Lisandro Centers Gleasonstad, KY 81367-1522
- Phone : 574.743.1203
- Company : O'Kon, Kemmer and Runolfsson
- Job : Forming Machine Operator
- Bio : Aut unde in illo libero. Rerum inventore minus pariatur. Suscipit eius ab quidem.
Socials
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/kamron.johnson
- username : kamron.johnson
- bio : A eaque iure quisquam similique. Enim accusamus soluta sint.
- followers : 5192
- following : 2901
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/kjohnson
- username : kjohnson
- bio : Mollitia aut dolorem rerum inventore.
- followers : 295
- following : 1184
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@johnsonk
- username : johnsonk
- bio : Enim minima explicabo enim. Dignissimos a nostrum ad optio qui illum.
- followers : 181
- following : 1402
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/kamronjohnson
- username : kamronjohnson
- bio : Reiciendis et neque animi quam et necessitatibus quo. Fuga libero eligendi nostrum. Voluptatem asperiores provident distinctio laborum ut porro.
- followers : 434
- following : 2953
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/johnson2009
- username : johnson2009
- bio : Repellat autem in tempora ab iure dolor rerum. Vitae consequatur porro minus asperiores.
- followers : 2697
- following : 1820