Morse Scale For Fall Risk Assessment: The Ultimate Guide To Keeping Patients Safe
Imagine this: You're a nurse or healthcare worker, and one of your main responsibilities is to ensure patient safety. But how do you predict whether a patient is at risk of falling? Enter the Morse Fall Scale (MFS), a game-changing tool designed to assess and mitigate fall risks. This isn't just any scale; it's a scientifically-backed method that's been helping healthcare professionals worldwide for decades.
Now, let's be real here—falls in healthcare settings are no joke. They can lead to serious injuries, longer hospital stays, and even legal issues. That's why understanding the Morse Scale for fall risk assessment is crucial. In this article, we'll break it down step by step so you can confidently implement it in your practice.
Whether you're a seasoned healthcare professional or just starting out, mastering the Morse Scale will not only enhance patient safety but also give you peace of mind. So, buckle up, because we're about to dive deep into the world of fall risk assessment!
- Can I Take Acetaminophen With Claritin Your Ultimate Guide
- Dottir In Icelandic Discovering The Meaning Usage And Cultural Significance
What is the Morse Scale for Fall Risk Assessment?
The Morse Scale for Fall Risk Assessment is more than just a checklist; it's a comprehensive tool designed to identify patients who are at high risk of falling. Developed by Dr. Judith Morse back in the 1980s, this scale has become a staple in hospitals and healthcare facilities around the globe. Its purpose? To help healthcare providers intervene early and prevent falls before they happen.
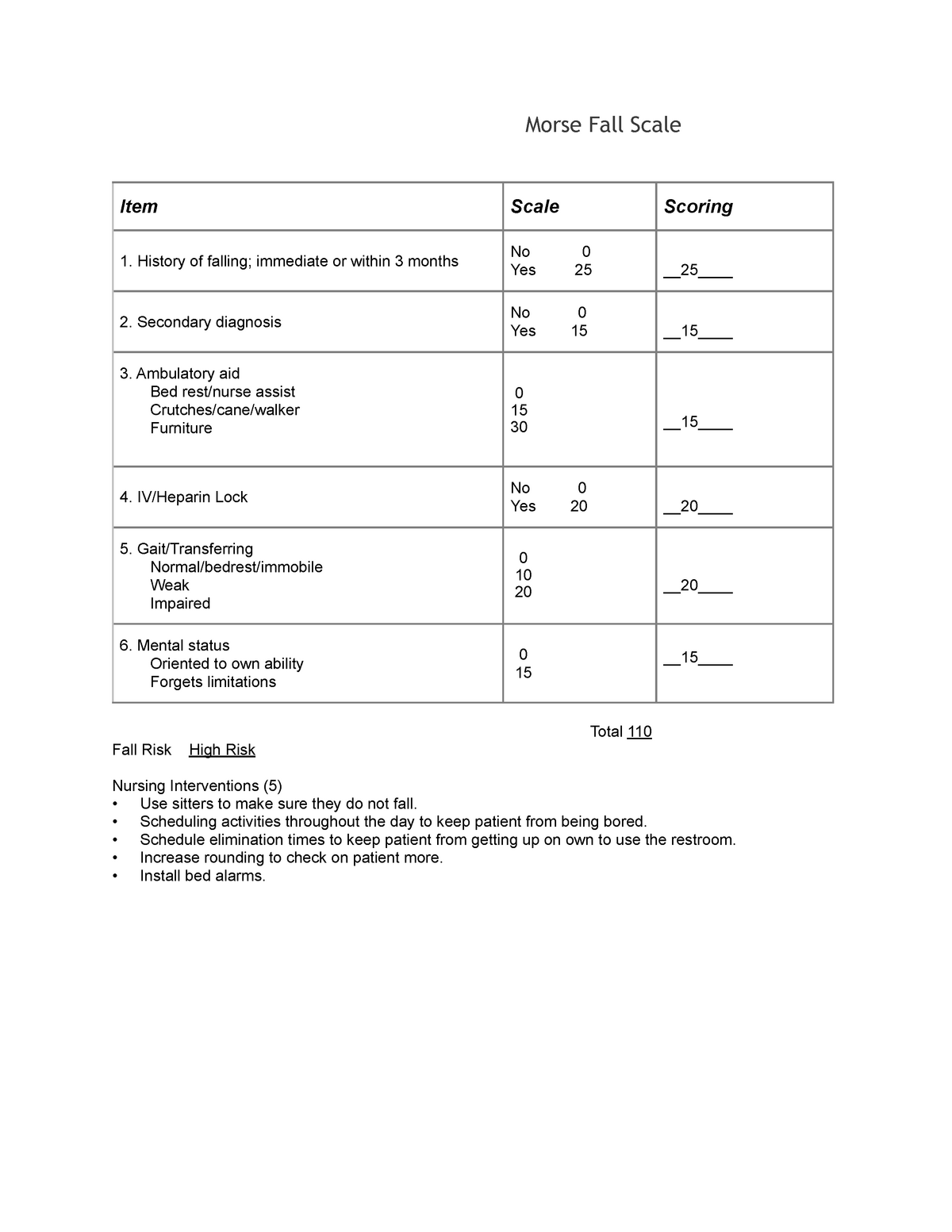
Here's the deal: The Morse Scale evaluates six key factors that contribute to fall risks. Each factor is scored, and the total score determines the level of risk. Simple, right? Well, not exactly. While the concept is straightforward, applying it effectively requires a solid understanding of each factor and how they interact.
Let's break it down further. The six factors assessed by the Morse Scale include: history of falling, secondary diagnosis, ambulatory aids, IV therapy, gait, and mental status. Each factor is assigned a specific score, and the sum of these scores determines the patient's risk level. A score of 25 or higher indicates a high risk of falling, while anything below that suggests a low risk.
- Old Bath And Body Works Scents A Journey Back To The Classics
- Unveiling The Iconic Jean Shrimpton Model Photos A Journey Through Time
Why is the Morse Scale Important?
Let me ask you something: Have you ever had a patient fall under your watch? If you have, you know how stressful and potentially dangerous it can be. Falls aren't just inconvenient; they can lead to fractures, head injuries, and even death in severe cases. That's where the Morse Scale comes in—it's like a superhero for patient safety.
By identifying high-risk patients early, healthcare providers can implement targeted interventions to reduce the likelihood of falls. This not only improves patient outcomes but also saves healthcare facilities time and money. Think about it: fewer falls mean shorter hospital stays, lower medical costs, and a better overall experience for patients and staff alike.
And let's not forget the legal implications. Falls can lead to lawsuits, which no one wants to deal with. By using the Morse Scale, healthcare providers can demonstrate due diligence in preventing falls, reducing the risk of legal action.
How to Use the Morse Scale Effectively
Alright, so you know what the Morse Scale is and why it's important. But how do you actually use it? Here's a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
First, gather all the necessary information about the patient. This includes their medical history, current medications, mobility status, and cognitive function. Once you have all the details, it's time to score each factor on the Morse Scale.
- History of Falling: Has the patient fallen in the past six months? If yes, assign a score of 25.
- Secondary Diagnosis: Does the patient have any conditions that could affect their balance or mobility? If yes, assign a score of 15.
- Ambulatory Aids: Does the patient use a cane, walker, or other assistive devices? If yes, assign a score of 15.
- IV Therapy: Is the patient receiving IV therapy? If yes, assign a score of 15.
- Gait: Does the patient have an abnormal gait? If yes, assign a score of 10.
- Mental Status: Does the patient have impaired mental status? If yes, assign a score of 15.
Add up all the scores to determine the patient's total risk level. If the score is 25 or higher, implement fall prevention strategies immediately. These might include bed alarms, non-slip socks, or increased supervision.
Understanding the Scores
Now that you know how to calculate the Morse Scale score, let's talk about what those numbers really mean. A score of 0-24 indicates a low risk of falling, while a score of 25 or higher suggests a high risk. But what does this mean for patient care?
For low-risk patients, regular monitoring and standard precautions are usually sufficient. However, for high-risk patients, more intensive interventions are necessary. This might involve hourly rounding, one-on-one supervision, or even restraints in extreme cases.
Remember, the goal isn't just to prevent falls—it's to ensure that patients feel safe and supported throughout their hospital stay. By using the Morse Scale effectively, you can achieve both.
Common Misconceptions About the Morse Scale
Let's clear up some common myths about the Morse Scale. First of all, it's not a one-size-fits-all solution. While the scale provides a solid framework for assessing fall risks, it's important to tailor interventions to each patient's unique needs. Some patients might require additional measures beyond what the scale suggests.
Another misconception is that the Morse Scale is only useful for elderly patients. While older adults are at higher risk of falling, falls can happen to anyone. That's why it's important to assess all patients, regardless of age or health status.
Finally, some people think that implementing the Morse Scale is time-consuming and complicated. In reality, it's a quick and efficient tool that can be easily integrated into daily routines. With a little practice, you'll be using it like a pro in no time.
Addressing Criticisms of the Morse Scale
No tool is perfect, and the Morse Scale is no exception. Some critics argue that it doesn't take into account all potential risk factors, such as environmental hazards or medication side effects. While this is true, the scale is meant to be a starting point, not the final word on fall prevention.
To address these limitations, healthcare providers can supplement the Morse Scale with additional assessments and interventions. This might include regular environmental audits, medication reviews, and patient education. By combining the Morse Scale with other strategies, you can create a comprehensive fall prevention plan.
Real-World Applications of the Morse Scale
Talking about the Morse Scale is one thing, but seeing it in action is another. Let's look at a few real-world examples of how the scale has been used to improve patient safety.
At a hospital in Texas, nurses implemented the Morse Scale as part of their routine assessments. Within six months, they saw a 30% reduction in patient falls. Similarly, a nursing home in Florida reported a 25% decrease in falls after adopting the scale.
These success stories aren't just flukes—they're proof that the Morse Scale works when used correctly. By taking the time to assess and address fall risks, healthcare providers can make a real difference in patient outcomes.
Case Studies
Let's dive into a couple of case studies to see how the Morse Scale can be applied in different scenarios.
Case Study 1: A 72-year-old woman with a history of falls and osteoporosis is admitted to the hospital for a hip replacement. Using the Morse Scale, the healthcare team identifies her as high risk and implements several interventions, including bed alarms and hourly rounding. The patient successfully completes her recovery without any falls.
Case Study 2: A 45-year-old man with a traumatic brain injury is admitted to the ICU. Despite having no prior history of falls, the Morse Scale identifies him as high risk due to his impaired mental status and abnormal gait. The healthcare team takes proactive measures, such as assigning a sitter and using a wheelchair for mobility. The patient avoids any falls during his stay.
Training and Education on the Morse Scale
So, you're sold on the Morse Scale, but how do you ensure that everyone on your team is using it correctly? Training and education are key. Start by providing comprehensive training sessions for all staff members who will be using the scale. This might include nurses, physical therapists, and even support staff.
In addition to formal training, consider creating quick reference guides and posters to keep the Morse Scale top of mind. Regular refresher courses and competency assessments can also help ensure that staff members are up to date on best practices.
Don't forget to encourage open communication and feedback. If staff members have questions or concerns about the Morse Scale, address them promptly. This will help build confidence and ensure consistent use of the tool.
Resources for Learning More
There are plenty of resources available to help you learn more about the Morse Scale. Start with the official Morse Fall Scale website, which offers a wealth of information on how to use the scale effectively. You can also check out peer-reviewed articles and case studies for real-world examples of its application.
For those looking to dive even deeper, consider attending conferences or workshops focused on fall prevention. These events often feature expert speakers and hands-on training sessions that can enhance your understanding of the Morse Scale.
Conclusion: Taking Action to Prevent Falls
Let's wrap things up, shall we? The Morse Scale for fall risk assessment is an invaluable tool for healthcare providers looking to improve patient safety. By identifying high-risk patients early and implementing targeted interventions, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of falls.
But remember, the Morse Scale is just one piece of the puzzle. To truly make a difference, you need to combine it with other strategies, such as environmental modifications and patient education. By taking a comprehensive approach to fall prevention, you can create a safer, more supportive environment for all patients.
So, what are you waiting for? Start implementing the Morse Scale in your practice today. And don't forget to share this article with your colleagues—knowledge is power, and the more people who understand the Morse Scale, the better off we all are.
Table of Contents
- What is the Morse Scale for Fall Risk Assessment?
- Why is the Morse Scale Important?
- How to Use the Morse Scale Effectively
- Common Misconceptions About the Morse Scale
- Real-World Applications of the Morse Scale
- Training and Education on the Morse Scale
- Conclusion: Taking Action to Prevent Falls


Detail Author:
- Name : Shawna Russel
- Username : delbert83
- Email : savion.mertz@schinner.com
- Birthdate : 1971-12-13
- Address : 845 Pascale Mall Suite 920 Schadenland, TX 62338
- Phone : +15095502360
- Company : Weber, Barton and Reichel
- Job : Industrial-Organizational Psychologist
- Bio : Rerum corporis inventore architecto necessitatibus itaque distinctio dolor. Saepe repellendus similique neque ab incidunt. Eos eos aut consequuntur et quo sapiente velit.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/nitzsche1995
- username : nitzsche1995
- bio : Molestiae in ratione doloremque.
- followers : 4993
- following : 2863
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/cristina_nitzsche
- username : cristina_nitzsche
- bio : Molestias aut at id at libero. Aut debitis rerum sed modi atque dolor. Modi est ratione fuga.
- followers : 1682
- following : 1611
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/cnitzsche
- username : cnitzsche
- bio : Voluptates minus debitis temporibus rerum. Dolorem possimus sed officia ducimus debitis laborum ex. Inventore quia modi quis.
- followers : 2511
- following : 540
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/cristina.nitzsche
- username : cristina.nitzsche
- bio : Voluptatem harum eum itaque. Et sapiente numquam sed soluta voluptate.
- followers : 6981
- following : 2580